Frequently asked questions
We know that this is confusing and hope these answers help
Some of our most frequently asked questions
Click on the frequently asked question to reveal the answer. If you have any queries, you can alwayscontact us.
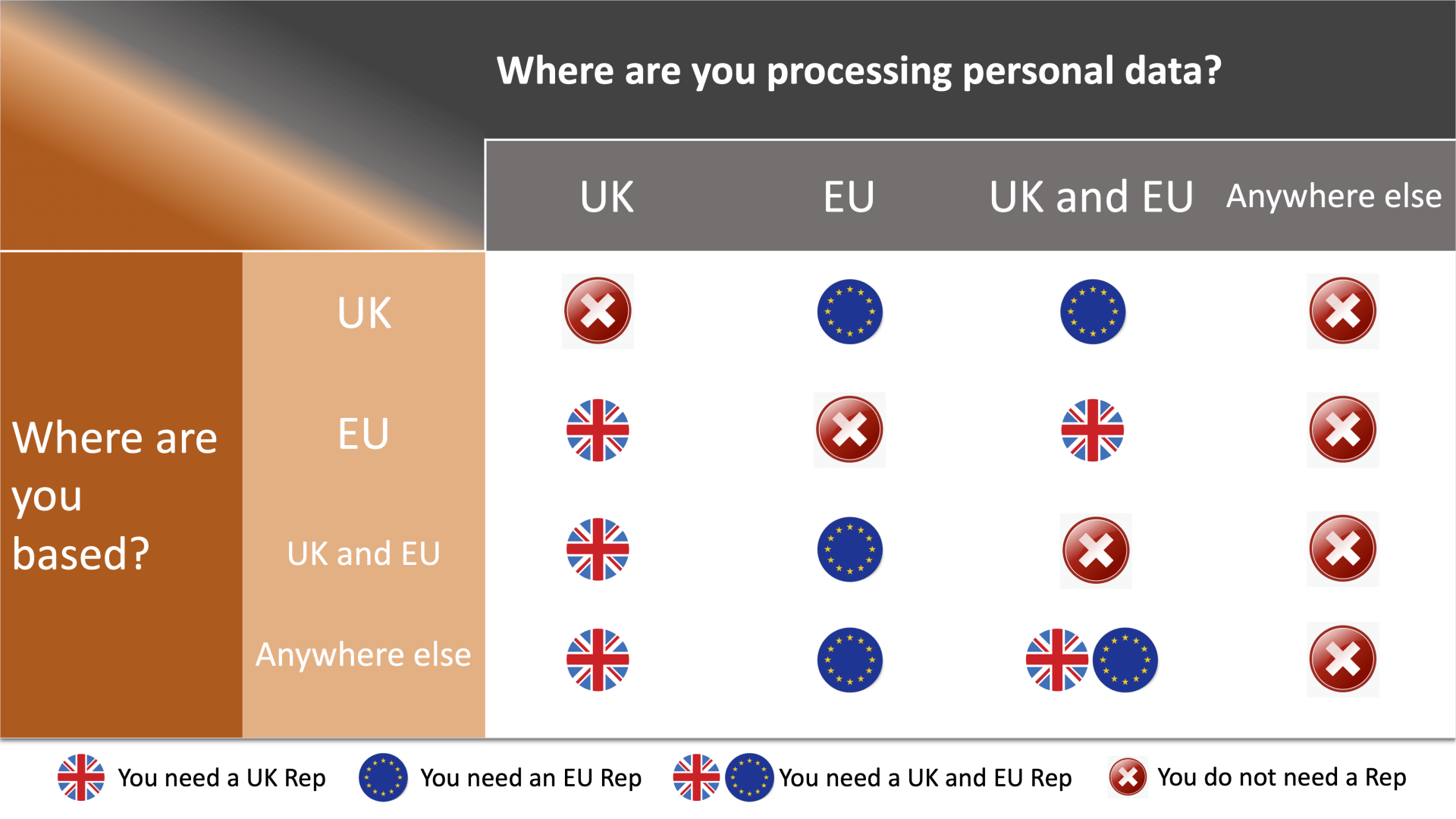
Do I need a Data Protection Representative to comply with the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)?
In more detail
Click the statement under the heading that best suits your organisation to see whether you need to appoint a Data Protection Representative
- I process UK and EU data
Yes, it is likely that you need a UK and European Data Protection Representative.
Any organisation that is not based within the UK and Europe, but does process personal information about people in or from those territories, must appoint a data protection representative that is based there to comply with data protection law.
- I process UK data, but not EU data
Yes, it is likely that you need a UK Data Protection Representative, but not a European Data Protection representative.
Any organisation that is not based within the UK, but does process personal information about people in or from the UK, must appoint a Data Protection Representative that is based there to comply with data protection law.
If you do not process persoanal information belonging to people in or from Europe, then you will not need a Data Protection Represenative in Europe aswell.
- I process EU data, but not UK data
Yes, it is likely that you need a European Data Protection Representative, but not a UK Data Protection representative.
Any organisation that is not based within the EU, but does process personal information about people in or from the EU, must appoint a Data Protection Representative that is based there to comply with data protection law.
If you do not process persoanal information belonging to people in or from the UK, then you will not need a Data Protection Represenative in UK aswell.
- I process data, but not UK or EU data
No you do not need a Data Rep.
This law only applies to organisations that do processes personal information belonging to people in or from the United Kingdom (UK) and Europe (EU).
- I do not process personal data
No you do not need a Data Rep.
This law only applies to organisations that do processes personal information belonging to people in or from the United Kingdom (UK) and Europe (EU).
- I process UK and EU data
No you do not need a Data Representative.
This is because you are based in both the United Kingdom and Europe.
This law only applies to organisations that are not based in the United Kingdom (UK) and Europe (EU).
You may need to appont a Data Protection Officer if you are processing personal data belonging to people in or from the United Kingdom (UK) and Europe (EU).
- I process UK data, but not EU data
No you do not need a Data Representative.
This is because you are based in both the United Kingdom and Europe.
This law only applies to organisations that are not based in the United Kingdom (UK) and Europe (EU).
You may need to appont a Data Protection Officer if you are processing personal data belonging to people in or from the United Kingdom (UK).
- I process EU data, but not UK data
No you do not need a Data Representative.
This is because you are based in both the United Kingdom and Europe.
This law only applies to organisations that are not based in the United Kingdom (UK) and Europe (EU).
You may need to appont a Data Protection Officer if you are processing personal data belonging to people in or from Europe (EU)).
- I process data, but not UK or EU data
No you do not need a Data Rep.
This law only applies to organisations that do processes personal information belonging to people in or from the United Kingdom (UK) and Europe (EU).
- I do not process personal data
No you do not need a Data Rep.
This law only applies to organisations that do processes personal information belonging to people in or from the United Kingdom (UK) and Europe (EU).
- I process UK and EU data
Yes, it is likely that you need a European Data Protection Representative.
Any organisation that is not based within Europe, but does process personal information about people in or from Europe, must appoint a data protection representative that is based there to comply with data protection law.
- I process UK data, but not EU data
No you do not need a Data Representative.
This is because you are based in the United Kingdom.
This law only applies to organisations that are not based in the United Kingdom.
You may need to appont a Data Protection Officer if you are processing personal data belonging to people in or from the United Kingdom (UK).
- I process EU data, but not UK data
Yes, it is likely that you need a European Data Protection Representative.
Any organisation that is not based within Europe, but does process personal information about people in or from Europe, must appoint a data protection representative that is based there to comply with data protection law.
- I process data, but not UK or EU data
No you do not need a Data Rep.
This law only applies to organisations that do processes personal information belonging to people in or from the United Kingdom (UK) and Europe (EU).
- I do not process personal data
No you do not need a Data Rep.
This law only applies to organisations that do processes personal information belonging to people in or from the United Kingdom (UK) and Europe (EU).
- I process UK and EU data
Yes, it is likely that you need a UK Protection Representative.
Any organisation that is not based within the UK , but does process personal information about people in or from the UK, must appoint a data protection representative that is based there to comply with data protection law.
- I process UK data, but not EU data
Yes, it is likely that you need a UK Protection Representative.
Any organisation that is not based within the UK , but does process personal information about people in or from the UK, must appoint a data protection representative that is based there to comply with data protection law.
- I process EU data, but not UK data
No you do not need a Data Representative.
This is because you are based in Europe.
This law only applies to organisations that are not based in Europe (EU).
You may need to appont a Data Protection Officer if you are processing personal data belonging to people in or from Europe (EU)).
- I process data, but not UK or EU data
No you do not need a Data Rep.
This law only applies to organisations that do processes personal information belonging to people in or from the United Kingdom (UK) and Europe (EU).
- I do not process personal data
No you do not need a Data Rep.
This law only applies to organisations that do processes personal information belonging to people in or from the United Kingdom (UK) and Europe (EU).
- Do I need a Data Protection Representative?
Any organisation that processed personal data in the UK and/or Europe, but is not based there, must appoint a data protection representative by law in most circumsntaces.
See our guidance here.
- What is a Data Protection Representative?
A Data Protection Representative is a company that you appoint under a written agreement to represent you in the country where you are processing personal data but not based.
In most cases where you are processing personal data in Europe or the United Kingdom but you are not based there, you will have to appoint a local representative by law.
- What does a Data Protection Representative do?
Your Data Protection Representative must perform certain functions for you. You will name them as the point of contact in the territory that they represent you in and they will be your first point of contact for data subjects and regulators.
Your Data Protection Representative will also keep a copy of your record of processing activities and cooperate with local the supervisory authorities on your behalf.
Customers of Data Rep Service also get a certificate so that they can show that they are complying with the legal requirement to appoint a representative, a guide to complying with UK and European regulations and templates for your privacy notice.
- What does the law say about appointed a Data Protection representative?
If you are not based in the UK or Europe and you monitor, or offer goods or services to people there, you will need to appoint a Data Protection Representative by law unless you are a public authority or your processing is only occasional.
You will need to authorise the representative, in writing, to act on your behalf regarding your EU GDPR compliance, and to deal with any supervisory authorities or data subjects in this respect.
Your representative may be an individual, or a company or organisation established in the country where you are processing.
You should give details of your representative to your UK and EU based data subejcts. This may be done by including them in your privacy notice or in the upfront information you give them when you collect their data.
Having a representative does not affect your own responsibility or liability to compluy with regulations.
- What is personal data?
Personal data is information relating to people that can be used to identify them, such as their name (even if it forms part of an email address) and their contact information, such as a telephone number, their home address or their email address.
Personal data may also include special categories of personal data or criminal conviction and offences data. These are considered to be more sensitive and you may only process them in more limited circumstances.
Information about companies or public authorities is not personal data.
However, information about individuals acting as sole traders, employees, partners and company directors where they are individually identifiable and the information relates to them as an individual may constitute personal data.
- What is classed as processing?
Any operation performed on personal data, whether directly or by automated means, including: collection, recording, organisation, structuring, storage, adaptation or alteration, retrieval, consultation, use, disclosure by transmission, dissemination or otherwise making available, alignment or combination, restriction, erasure or destruction of personal data on behalf of the data controller.
- Why have I not heard of this legal requirement?
The regulations came into force in May of 2018 and they have not been widely publicised outside the United Kingdom or Europe where they apply.
- We have appointed a Data Protection Officer... Do we still need to appoint a Data Protection Representative?
Yes you may have to appoint a Data Protection Representative in addition to your Data Protection Officer.
The data protection officer role is different from the role of a data protection representative.
- What could happen if we do not appoint a Data Protection Representative?
The penalties for non-compliance with the GDPR can be high. You can be fined up to the greater of €20 million or 4% of your worldwide annual turnover and regulators can impose orders stopping you from processing personal data.
For failing to appoint a Data Protection Representative when one is required, the penalty can be up to €10 million or 2% of total worldwide annual turnover, whichever is higher.
- What countries can Data Rep Service represent me in?
Data Rep Service can be appointed as your Data protection representative in any or all of the following territories:
Austria
Belgium
Bulgaria
Croatia
Republic of Cyprus
Czech Republic
Denmark
Estonia
Finland
France
Germany
Greece
Hungary
Ireland
Italy
Latvia
Lithuania
Luxembourg
Malta
Netherlands
Poland
Portugal
Romania
Slovakia
Slovenia
Spain
Sweden
United Kingdom
- Where does my Data Protection Representative have to be based?
Your data protection representative must be based in the territory where you are processing personal data whether that's Europe or the United Kingdom.
Data Rep Service is based in both Europe and the United Kingdom so can represent you in all of the territories where you need a representative.
- My business is not based in Europe or the United Kingdom, so how can these regulations apply to me?
The regulations apply to all organisations that process personal data in the United Kingdom and Europe no matter where they are based in the world.
- How does Brexit affect the need for a Data Protection Representative in Europe and the United Kingdom?
The rules will still apply no matter what effect Brexit has.
If you are based outside both the United Kingdom and Europe, you will need a representative in both of these territories.
If you are a UK business that processes personal data in Europe, you will have to appoint a data representative in Europe.
and if you are a European business that processes personal data in the UK you will have to appoint a representative in the UK.
Data Rep service have offices in both the UK and Europe so we can represent you in both territories No matter where you are based.
- How can I get a Data Protection Representative?
- Will my Data Protection Representative be liable for fines and penalties handed to me by a regulator?
You remain liable to comply with all regulations and you remain liable for any fines or penalties haded to you by any regulators.
The regulations clearly state that the designation of a representative does not affect the responsibility or liability of the company which appoints them.
- How much does a Data Protection Representative cost?
- How quickly can Data Representative Service be set up?
Your service will usually commence on the next working day , but if your requirement is extremely urgent you can let us know and we can set you up on the same day.
- How can I pay for my Data Representative Service?
You can pay us by bank transfer on receipt of an invoice in dollars ($) euro's (€) or pounds (£) and we can discuss other currencies on demand.
You can either pay the full annual balance or you can pay by monthly instalments at no extra cost.
If it’s more convenient for you, you can pay using Mastercard, Visa or paypal too, or take take advantage of our Direct Debit facility too.
- How can Data Rep Service help me pass diligence processes by UK and EU Companies?
If you are being examined by another organisation to cheque that you have adequate systems processes and policies in place to comply with data protection regulations you will be able to show them the certificate to demonstrate that you have appointed data wrap service as your GDP are article 27 representative.
You may also benefit from our compliance tool kit, which is available here.
Common Data Protection Terms explained
Click on the word or term to reveal the meaning. If you have any queries, you can always contact us.
- Accountability
The data protection principle that says data controllers must demonstrate compliance with the data protection principles.
- Accuracy
The data protection principle that says data must be accurate and kept up to date. You must take every reasonable step to ensure that inaccurate personal is erased or rectified immediately.
- Call
A connection using a telephone service allowing two-way communication in real time.
- CCTV
Closed Circuit Television, which is in use across the Branch Network and head Office for the purpose of safety and crime prevention.
- Consent
Of the data subject means freely given, specific, informed and unambiguous indication of the data subject's wishes by which he or she, by a statement or by a clear affirmative action, signifies agreement to the processing of personal data relating to him or her.
- Consent request
A request from the business directed at data subjects, asking for their permission to process their data and informing them of the purpose.
- Controller
The organisation that determines the purposes and means of the processing of personal data.
- Data breach
A breach of security leading to the accidental or unlawful destruction, loss, alteration, unauthorised disclosure of, or access to, personal data transmitted, stored or otherwise processed.
- Data concerning health
Personal data related to the physical or mental health of a person, including the provision of health care services, which reveal information about his or her health status.
- Data minimisation
The data protection principle saying that data must be adequate, relevant and limited to what is necessary in relation to the purposes for which they are processed.
- Data Protection Act 1998
A set of data protection regulations in the United Kingdom that were in force between 1998 and 2018, when they were replaced by the Data Protection Act 2018, the Data Protection, Charges and Information Act 2018 and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
- Data protection Act 2018
The new UK Data Protection Act that sits alongside the Uk Data Protection, Charges and Information Acrt 2018, the General Data Protection Regulations (GDPR) and the Privacy in Electronic Communications Regulations (PECR) (Updated by the E-Privacy Bill) to form the new standard of Data Protection in the UK since 25th May 2018.
- Data Protection, Charges and Information Act 2018
The regulation that sits alongside the Data Protection Act 2018 covering the rules around registering as a data controller in the UK.
- Data Protection Officer
The person legally appointed by an organisation to ensure that they know the rules and comply with all of them.
- Data Protection Representative
A firm based within the territory that has been appointed by a processor or controller to represent them in that country to comply with the legal requirement to have a representative.
- Data sharing protocol
An internal document that enables lawful sharing of personal data across the group provided that there is a reason to share.
- Data Subject
A person whose data you are processing.
- Data Subject Access Request (DSAR)
A request from a person to see a copy of the personal information we hold about them.
- Direct marketing communications
Any form of advertising, whether written or oral, sent to one or more people by automated calling and communication systems including email, telephone and SMS.
- Direct marketing voice-to-voice calls
Live telephone calls without the use of automated calling systems and communication systems.
- Due diligence
A comprehensive appraisal of a business undertaken to establish that it meets the required standards to enter into a contract with.
- E Privacy bill (ePr)
The proposed update to the Privacy in Electronic Communications Regulation (PECR).
- Electronic Communication
Any communication that is carried out using technology.
- Electronic communications content
The content of electronic communications services, such as text, voice, videos, images, and sound.
- Electronic mail
Any text, voice, sound or image message sent which can be stored in the network or by the recipient.
- Filing system
Any structured set of personal data, which is accessible according to specific criteria, whether centralised, decentralised or dispersed on a functional or geographical basis.
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
The General Data Protection Regulations (GDPR) is the Europe wide set of data protection regulations that became enforceable after 25th May 2018.
The rules will still apply to the United Kingdom post Brexit.
- Genetic data
Personal data relating to the inherited or acquired genetic characteristics of a natural person which give unique information about the physiology or the health of that natural person and which result, in particular, from an analysis of a biological sample from the natural person in question.
- Information Commissioners Office (ICO)
The United Kingdom’s Data Protection Authority is the Information Commissioners Office (ICO).
They are responsible to ensuring compliance to data protection regulations.
- Inform statement
The act of telling a data subject what data you will take form them and why.
- Integrity and confidentiality
The data protection principle that says data must be processed in a manner that ensures appropriate security of the personal data, including protection against unauthorised or unlawful processing and against accidental loss, destruction or damage, using appropriate technical or organisational measures.
- Lawfulness, fairness and transparency’
The data protection principle that says data must be processed lawfully, fairly and in a transparent manner.
- Location data
Any data processed in an electronic communications network, indicating the geographic position of the user.
- Object
The act of saying something to express one's opposition to or disagreement with something.
- Privacy in Electronic Communications Regulation (PECR)
Privacy in Electronic Communications regulations (PECR) is a Europe wide set of regulations concerning the use of electronic communications that have been in place since 2003.
The regulations will be update by the e-privacy bill.
- Personal data
Any information relating to a person such as a name, an identification number, location data, an online identifier or other factors such as their physical, genetic, mental, economic, cultural or social identity.
- Privacy Notice
The public facing document that contains all the information data subjects should know about how we use their personal data and their rights.
- Privacy policy
An internal policy that explains how your organisation manages personal data.
- Processing
Any operation that is performed on personal data, whether automatic or not, such as collection, recording, organisation, structuring, storage, adaptation, alteration, retrieval, consultation, use, disclosure, dissemination, making available, alignment or combination, restriction, erasure or destruction.
- Processor
An organisation that processes personal data on behalf of a controller.
- Profiling
Processing a data subject’s personal information to automatically decide or predict their personal preferences, interests, behaviour or movement.
- Recipient
An organisation to which personal data is disclosed.
- Record of Processing Activity
A record, required by law, that details what personal information an organistion processes and what the purpose and lawful basis is.
- Regulation General Data Protection (RGDP)
This is how certain countries refer to what is more widely known as the General Data Protection Regulations (GDPR), which is the Europe wide set of data protection regulations that became enforceable after 25th May 2018.
- Restriction of processing
The marking of stored personal data with the aim of limiting their processing in the future.
- Retention Schedule
A document listing all the titles of the records held the length of time each document or record will be retained, the reason for its retention. A clearly defined plan for a record retention and disposal is a vital component of a records program.
- Sub Processor
When a processor appoints another processor to process the controller’s data.
- Third party (Other)
An organisation other than your own that you deal with.
- Third party
An organisation other than the data subject, controller, processor and persons who, under the direct authority of the controller or processor, are authorised to process personal data.
- Written Agreement
A document between 2 parties that explains what each party is reponsible for.